Google Chrome, or just Chrome, is (at the time of writing) the most popular web browser by a fair amount. Twice as popular as Mozilla’s Firefox.
Chrome stores its artefacts in SQLite, JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) and SNSS (Session Saver) formats. The Artefact locations for Windows 7+ is
%USERPROFILE%\AppData\Local\Google\Chrome\User Data\Default
It is worth noting that SQLite files used by Chrome do not have file extensions.
Within the “visits” table of History, there is a “transitions” field. This shows how the page was visited. The values of this field are difficult to parse manually as they are stored in 32bit values, there are forensic tools (like Chromium, Woanware ChromeForensics or Nirsoft Chrome History View) which can be used to decode the values.
The transition values then relate to: 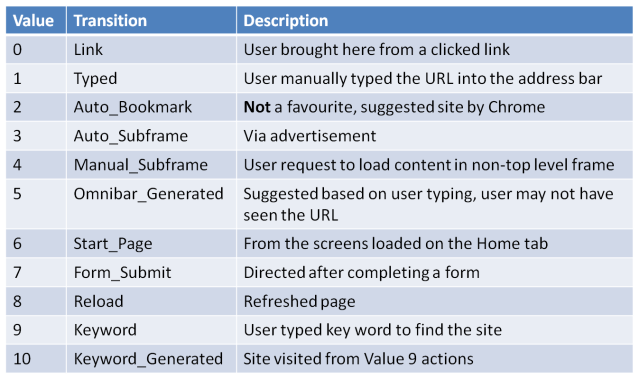
Timestamps
Chrome timestamps are stored in “Webkit” format which is the number of microseconds since 1st Jan 1601…. I know right?! Luckily DCode has a Chrome time decoder, there are other ways to figure it out. Which… feel free.

