As IE comes bundled with Windows as standard it is often the browser (of choice?) used by a lot of organisations. Larger organisations are also often slower to update IE, in my experience, as they have integrated business critical applications to an older version and do not see the urgency of the upgrade.
As such IE makes a perfect target for attackers seeking out businesses.
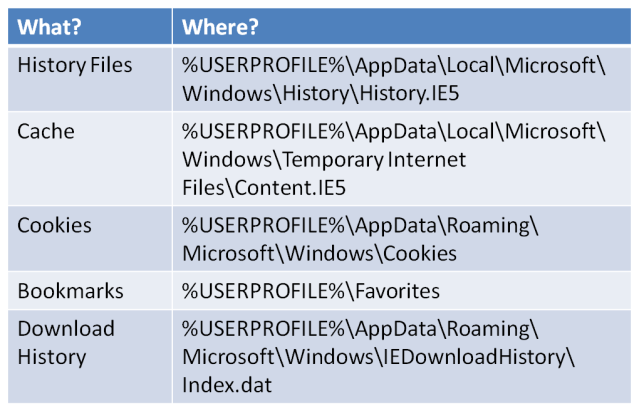
Windows 7
With previous versions of Windows the History files have pretty much remained the same, Windows 7 also uses something very similar to this system. The location does change from OS to OS though:
Windows 7 locations. It is also worth noting that a “low” folder exists when the browser is being used in “Protected Mode”, items in this folder are from unprivileged use.
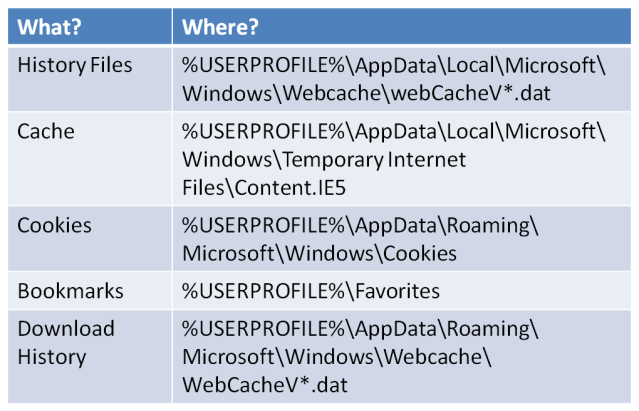
Windows 8
With Windows 8 there are a couple of changes, including the introduction of the “WebChache” folder and “WebCacheV*.dat” (the * will be replaced with a number). This is then extended into Windows 8.1
Both the History Files and the Download History have been moved to the .dat format.
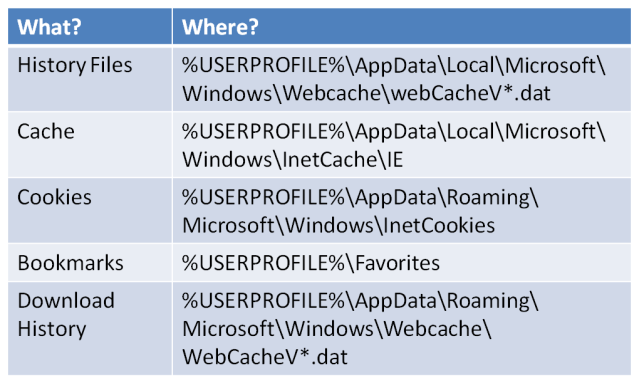
Windows 8.1
Finally we come to Windows 8.1, possibly another term for Windows 8 Service Pack 1, as discussed by Peter Bright.
Windows 8.1 pretty much finishes off the rest of the artefacts into .dat files leaving only the Bookmarks in the US spelling of Favourites, don’t get me started on the “US English or International English” debate!
Final note
As with the previous locations of these artefacts, the locations are hidden by default.